A Deflection of the Ridge Beam Is Called
In roof framing the base of the triangle is called the _____. Eaves rakes 2.

Reinforcing Floor Joists Article Image Timber Beams Flooring Remodeling Mobile Homes
The lower level edges of a gable roof are called the _____ and the sloped edges are called the _____ 1.

. I would use a deflection limit of L400 but no greater than 12mm for dead load. 1 No attic floor ceiling joists such as for a sloped cathedral ceiling. In each case the values of the deflection around a specified point are used to determinate the high-order derivatives of deflection at that point.
Overhanging joist example example no. Design a structural ridge beam to take the loads appropriate load width and install before they decouple the roof. Deflection of the ridge beam is called saddleback or swayback.
Deflection is a result from the load action to the beam self weight service load etc If the deflection value is too large the beam will bend and then fail. Saddleback or swayback B. One of the.
Ridge beam uniform load of 30 ll 40 tl outside bearing wall r1 r2. This condition generally results in lack of resistance to outward thrust force. Roof Deflection Sag And Creep.
A soffit that is attached directly to the underside of the rafter tails is called an _____ soffit. V deflections of the elastic curve. However a structural ridge beam may be required for several reasons as described in this section.
_____ is the deflection of the ridge beam. Value Use LL only DLLL Roof beams. Industrial L180 L120 Commercial plaster ceiling L240 L180 no plaster L360 L240.
_____ is the deflection of the ridge beam. Engineered by the LVL company accepted by City inspection. Ridge boards shall be at least.
The deflection is always zero at the supports and the deflection is maximum at the mid span of a symmetrically loaded simply supported beam. Deflection - this is definitely an important visual criteria and excessive sag can cause cracking in finishes. Ridge beam sizing is based on the span of the beam between supports and the amount of roof load supported by the beam.
EI d2y dx2 M E I d 2 y d x 2 M. Such members are called beam. If a gap exists between the.
The product EI is called flexural rigidity of the beam which is usually constant along the beam. The maximum deflection of beams occurs where slope is zero. Many shafts act simultaneously as torsion members and as beams.
In this case the L180 deflection of a 20 ridge beam is 066 inches. D Point of action of load. Hogback or horseback C.
A soffit that is attached directly to the underside of the rafter tails is called an enclosed soffit. This roof is composed of rafters which meet a center ridge beam. Beam deflection means the state of deformation of a beam from its original shape under the work of a force or load or weight.
You have probably seen this and it is most likely due to roof deflection sag and creep. The main members supporting floors of buildings are beams just as an axle of a car is a beam. Saddleback or swayback 2.
A ridge board is a non-structural member that serves as a prop for opposing rafters to rest against and connect to. Thanks McMark for clarifying the deflection issue. A ridge beam of 20 long supported on both ends will not have a L180 deflection approaching 132 inches because the deflection will be based on one half of 20.
A tie in the upper two-thirds of the rise is called a collar tie which although it adds some rigidity is too small to create a strong enough triangle to resist spread. Allowable Deflection Limits All building codes and design codes limit deflection for beam types and damage that could happen based on service condition and severity. Ridge sag is called deflection by construction professionals and is easy to spot from the ground when in an advanced stage but minor deflection is best caught by sighting down the ridge of the roof.
Ridge boards can only be used in roofs with slopes from 3 in 12 up to 12 in 12. When there is the vertical displacement at any point on the loaded beam it is said to be deflection of beams. As discussed in Chapter 9 Beam Deflection there are three methods of discretization forward backward and central difference methods.
Support for high ends of rafters is typically necessary for the following conditions. The center beam is probably not terribly thick. Therefore it is vital that deflection must be limited within the allowable values as stipulated in the Standards The theory and background of deflection comes from curvature.
The general and standard equations for the deflection of beams is given below. _____ is the deflection of the ridge beam. Select deflection limit for live and total loads enter uniform load on backspan letters are for load identification on print-out and notes enter uniform load on overhang in.
A step in the ridge may indicate structural problems. A gap between the wall and the soffit may indicate rafter sag or spread. A simply supported beam AB carries a uniformly distributed load of 2 kipsft over its length and a concentrated load of 10 kips in the middle of its span as shown in Figure 73aUsing the method of double integration determine the slope at support A and the deflection at a midpoint C of the beam.
The Slope Is Zero At The Maximum Deflection y max. Slope of the beam is defined as the angle between the deflected beam to the actual beam at the same point. A _____ tie is a tension tie in the upper third of opposing gable rafters that is intended to resist rafter separation from the ridge beam.
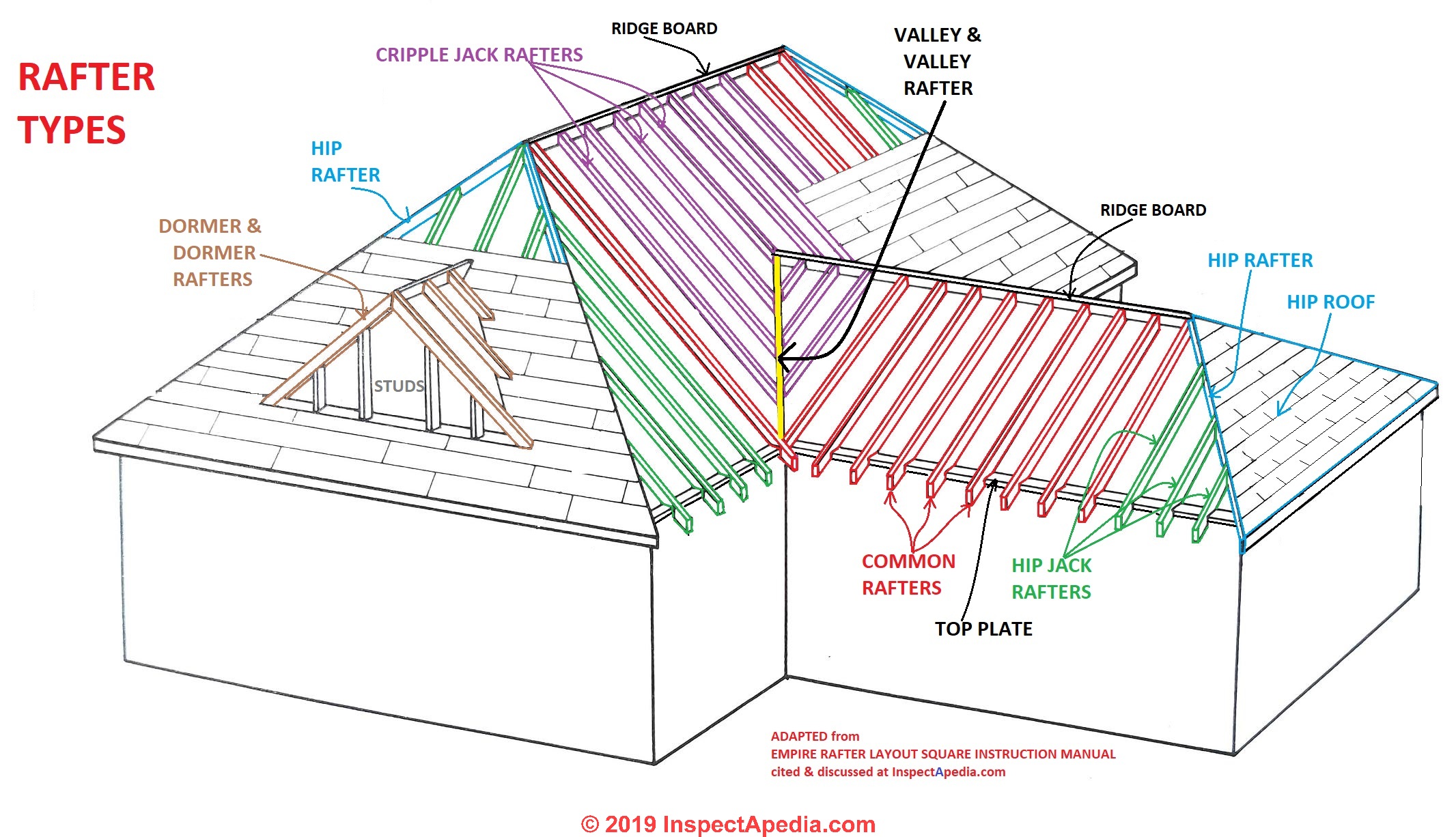
Roof Framing Definition Of Types Of Rafters Definition Of Collar Ties Rafter Ties Structural Ridge Beams Causes Of Roof Collapse Wall Spread

Collar Ties Vs Rafter Ties Internachi


0 Response to "A Deflection of the Ridge Beam Is Called"
Post a Comment